วิธีการออกแบบเพื่อลดการซับซ้อนของ software
ควรออกแบบให้เป็น Layer และ แต่ละ Layer ควรกำหนดจุดประสงค์ให้ชัดเจน
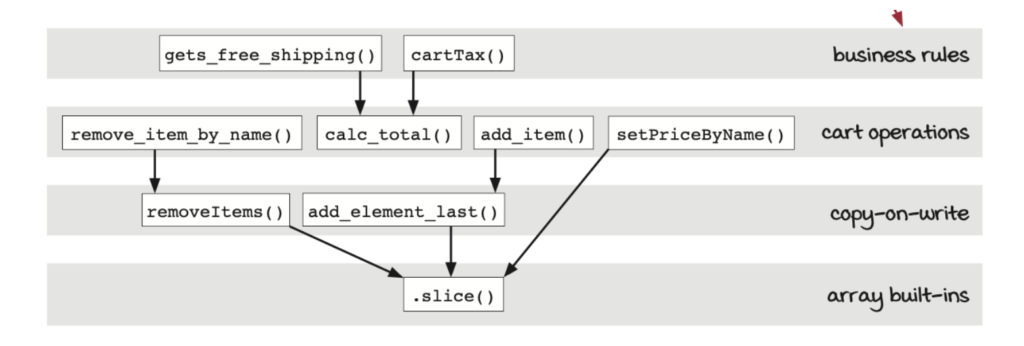
ภาพจากหนังสือ https://www.amazon.com/Grokking-Simplicity-software-functional-thinking/dp/1617296201
จากภาพด้านบนเราควรจะกำหนดวัตถุประสงค์ของแต่ละ layer ให้ชัดเจน และ call graph ก็ไม่ควรจะยุ่งเหยิง หรือมีลูกศรที่ข้าม layer และใน layer เดียวกันก็ไม่ควรจะมีที่เรียกกันเอง ( ถ้า function นั้นๆ เรียก function ใน layer เดียวกัน function นั้นก็ต้องอยู่บน layer ที่สูงกว่า )
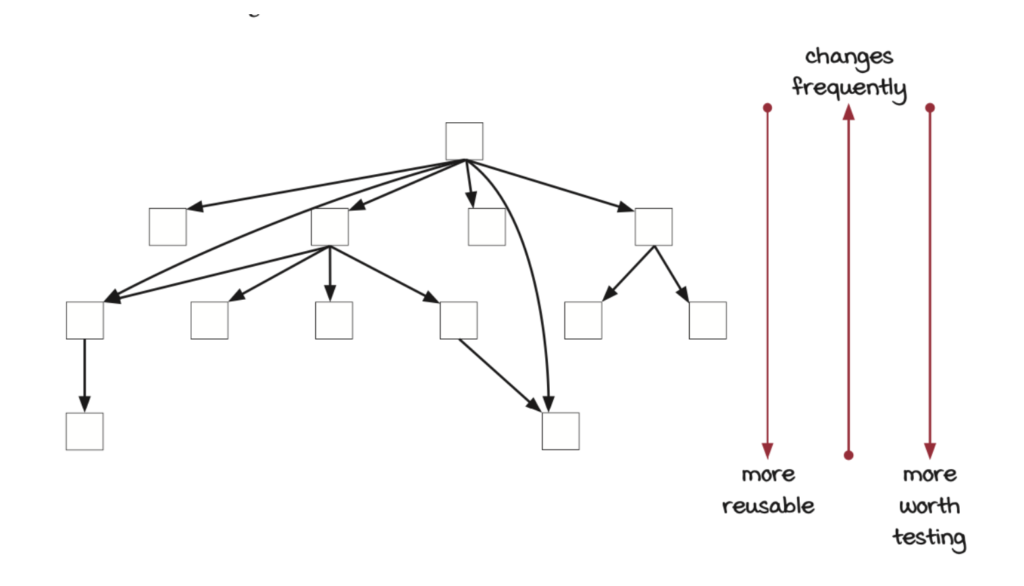
Layer ที่อยู่ต่ำ คือ layer ที่เรียกใช้ function library ของภาษา หรือ system call ของ os ส่วน function ที่อยู่ชั้นบน คือ business domain layer ซึ่ง layer ที่อยู่ด้านบนถัดไปของ business domain layer ไม่สมควรที่จะรับรู้ data structure
Function ที่อยู่ layer บนมันจะเป็น function ที่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงบ่อย มากกว่า function ที่อยู่ layer ต่ำกว่า
Function ที่อยู่ layer ด้านล่าง จะถูกใช้งานในหลายๆ function ที่อยู่ใน layer ที่สูงกว่า
Function ที่คุ้มค่าสำหรับ testing คือ function ที่อยุ่ใน layer ล่างๆ เพราะ เป็น function ที่ถูกเรียกใช้บ่อยจาก function ที่อยู่ใน layer ที่สูงกว่า
Get in Touch with us
Related Posts
- AI会在2026年取代软件开发公司吗?企业管理层必须知道的真相
- Will AI Replace Software Development Agencies in 2026? The Brutal Truth for Enterprise Leaders
- 使用开源 + AI 构建企业级系统(2026 实战指南)
- How to Build an Enterprise System Using Open-Source + AI (2026 Practical Guide)
- AI赋能的软件开发 —— 为业务而生,而不仅仅是写代码
- AI-Powered Software Development — Built for Business, Not Just Code
- Agentic Commerce:自主化采购系统的未来(2026 年完整指南)
- Agentic Commerce: The Future of Autonomous Buying Systems (Complete 2026 Guide)
- 如何在现代 SOC 中构建 Automated Decision Logic(基于 Shuffle + SOC Integrator)
- How to Build Automated Decision Logic in a Modern SOC (Using Shuffle + SOC Integrator)
- 为什么我们选择设计 SOC Integrator,而不是直接进行 Tool-to-Tool 集成
- Why We Designed a SOC Integrator Instead of Direct Tool-to-Tool Connections
- 基于 OCPP 1.6 的 EV 充电平台构建 面向仪表盘、API 与真实充电桩的实战演示指南
- Building an OCPP 1.6 Charging Platform A Practical Demo Guide for API, Dashboard, and Real EV Stations
- 软件开发技能的演进(2026)
- Skill Evolution in Software Development (2026)
- Retro Tech Revival:从经典思想到可落地的产品创意
- Retro Tech Revival: From Nostalgia to Real Product Ideas
- SmartFarm Lite — 简单易用的离线农场记录应用
- OffGridOps — 面向真实现场的离线作业管理应用














